Integrating in-situ CO2 removal at high temperature by solid sorbents during sorption-enhanced steam reforming process for high-purity hydrogen production has been considered to change the normal equili- brium limits of shift reactions and increase hydrocarbon conversion as well as reduce CO2 emissions. How- ever, a difficulty by integrating these reaction steps in a single and integrated process involves selecting suitable sorbents and reaction conditions under which all of the processes can be carried out. Due to the difficulty in application of solid sorbents in SERP, the improvement of their performance is crucial to make the process important for industrial applications.This study discussed the performances of CaO, MgO, hydrotalcite and Li2ZrO3 based sorbents during sorption-enhanced steam reforming for high-purity hydrogen production,while different methods for enhancing these sorbents activities were summarized.The factors of reaction conditions such as temperature,pressure,the amount of water vapor etc. and related reaction mechanisms using these solid sorbents are identified. CaO has shown its potentials with its lost cost and high capacities. Nevertheless,the deactivation of CaO during multi-cycles carbonation-regeneration is challenging for con- tinuous long-term operating conditions for hydrogen production from catalytic steam reforming.The potential and development of the multifunctional sorbent–catalyst materials having a dual function of cata- lytic steam reforming and in-situ CO2 removal were discussed.
Conclusions
A comprehensive overview of the current status of the solid sorbent alternatives for in-situ CO2 removal related to the sorption-enhanced steam reforming process for high-purity hydrogen production has been discussed.And sorbents performances under various operating conditions according to the related mechanisms have been summarized. As described, low selectivity and low capacity of the available sorbents may not make the process effective enough for sorption-enhanced steam reforming process for hydrogen production.Chemical looping method applied in hydrogen production for the sorbents possessed with reliability, stability and removal efficiency are main challenges. CaO has shown its potentials with its low cost and high capacities. However, these lection of sorbents should be careful and objective, and more efforts should be made to reduce uncertainty and bias before implementation.It is reasonable to believe that significant breakthroughs and a significant increase in the number of sorbents and methods on in-situ CO2 removal related to sorption-enhanced steam reforming process will occur in the coming future.
The results have been published on Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 53 (2016) 536–546.
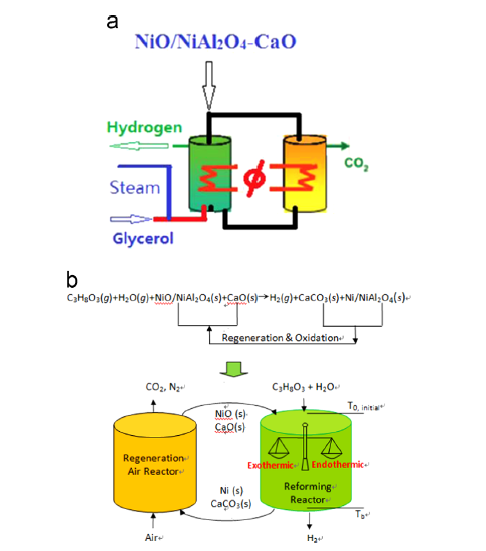
Fig. 1. High purityhydrogenproductionsystemfromsteamreforming:
(a) sorption-enhancedsteamreformingprocessintegratingin-situCO2 removal;
(b) sorption-enhancedchemical-loopingsteamreformingprocessintegratingin- situ CO2 removals.