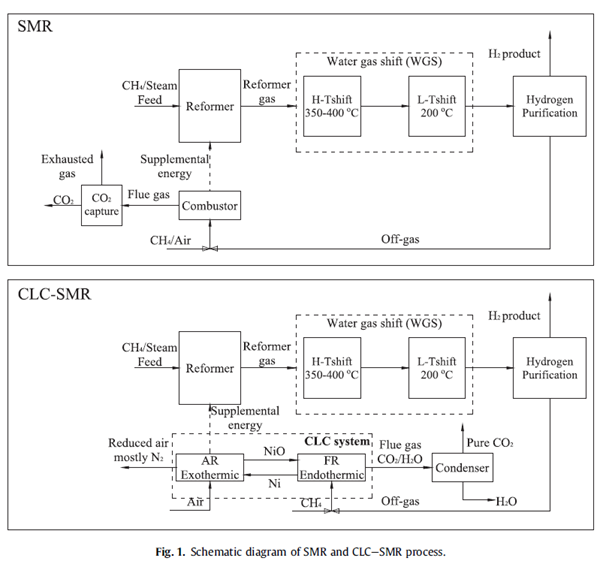
This paper investigates the benefits of chemical looping combustion (CLC) thermally coupled with steam methane reforming (SMR) process (CLC-SMR) over conventional SMR process by means of exergy analysis. The conventional combustor of SMR is replaced by employing CLC system in order to achieve cleaner production of hydrogen through eliminating energy penalty associated with capturing CO2 from combustion flue gas and reducing exergy destruction during combustion process. The overall exergy efficiency of SMR and CLC-SMR was calculated equal to 65.2% and 71.4%, respectively, approximately 9.5% of exergy efficiency was increased from CLC-SMR. Analyses were extended to investigate the individual exergy efficiency of each component in both processes. In SMR the main parts of exergy destroyer were localized in combustor and CO2 capture unit with a contribution of 28.5% and 24.9% of the total exergy destroyed, respectively. In CLC-SMR process, the overall exergy destruction was reduced to 217.9 compared with that of 299.7 kJ per mol of CH4 used in SMR. The exergy efficiency of combustion process in SMR and CLC-SMR was calculated equal to 78.0% and 76.5%, respectively, correspondingly reducing exergy destruction from 85.3 in conventional combustor to 79.1 in CLC kJ per mol of CH4 used. A preliminarily financial analysis was involved further to examine the economic feasibility of CLC-SMR process.
Conclusions
In this work, a comparative exergy analysis between novel chemical looping combustion thermally coupled with steam methane reforming (CLC-SMR) and conventional steam methane reforming (SMR) processes has been presented. Thermally coupling chemical looping combustion (CLC) and SMR provides potential possibilities for both eliminating CO2 capture penalty and reducing the exergy destruction in combustion process. The overall exergy efficiency increases by 9.5 percentage points compared to conventional SMR in the case of CLC-SMR. The exergy efficiency of combustion (77.96%) obtained in CLC-SMR increases by 1.47% than that in SMR (76.49%), and the exergy destruction within CLC has been decreased by 7.3%. Furthermore, a comparative financial analysis is involved and the economic feasibility of this novel CLC-SMR process is demonstrated. Although a preliminarily comparative analysis between popular SMR and this novel CLC-SMR has demonstrated the feasibility of this suggested process from the perspective of both thermodynamic and financial aspects, a more systematical analysis is farreaching in terms of considering kinetic factors and rendering a full chain energy analysis. For industrial application, CLC-SMR simplifies the overall process as well as the complicated equipment for CO2 capture, leading to recovery of sequestration-ready CO2 and obtaining of cleaner production of hydrogen.
The results have been published on Journal of Cleaner Production 131 (2016) 247-258.