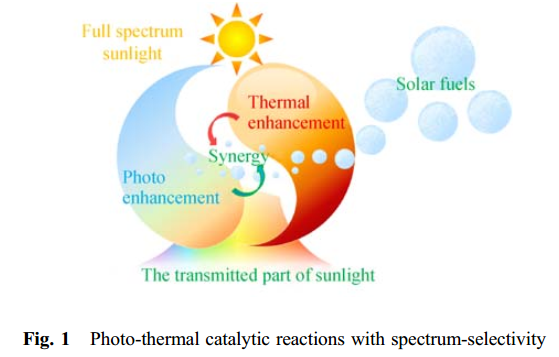
Solar fuel is one of the ideal energy sources in the future. The synergy of photo and thermal effects leads to a new approach to higher solar fuel production under relatively mild conditions. This paper reviews different approaches for solar fuel production from spectrum-selective photo-thermal synergetic catalysis. The review begins with the meaning of synergetic effects, and the mechanisms of spectrum-selectivity and photo-thermal catalysis. Then, from a technical perspective, a number of experimental or theoretical works are sorted by the chemical reactions and the sacrificial reagents applied. In addition, these works are summarized and tabulated based on the operating conditions, spectrum-selectivity, materials, and productivity. A discussion is finally presented concerning future development of photo-thermal catalytic reactions with spectrum-selectivity.
Conclusions:
The photo-thermal catalytic reactions with spectrum-selectivity are emerging methods of solar fuel production. Photo-thermal catalysis is the synergetic effect rather than the superposition of photo and thermal catalyzes. Performances of photo-thermal catalysis are usually reported to be higher than photo or thermal catalysis, while the underlying mechanism remains unclear and needs further exploration. Due to its spectrum selective nature, the photo-thermal catalysis reaction is more applicable in full-spectrum solar energy systems when coupled with PV arrays or power cycles. According to Section 3, such reactions produce solar fuels from a wide variety of reactants, such as biomass, fossil fuels, sewages, water and CO2, which suggests the feasibility satisfying the industrial requirements in nowadays and the future. As a newly-proposed type of reaction, spectrum-selective photo-thermal catalytic reaction yet demands for more academic attentions. Research directions may be as follows:
1) Optimizations on materials and structure of catalysts are needed to achieve a higher conversion efficiency and selectivity of products.
2) Consider the integration with other energy conversions, simple and cheap ways to alter catalyst light absorption should be developed.
3) Deeper understanding of the reaction mechanism, especially the photo-thermal synergy effects, is expected to be explored.
4) Elevated temperature is likely to induce deactivation of catalysts. Therefore, high-temperature durability is expected.
The results have been published on Front. Energy 2017, 11(4): 437-451.