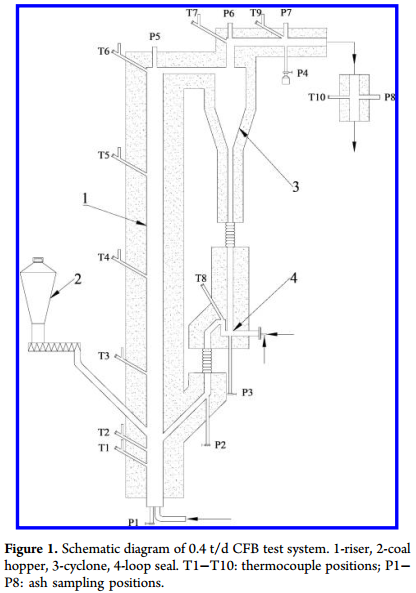
Zhundong coal (ZDc) with a large reserve is faced with severe slagging and fouling during combustion in pulverized coal furnaces because of its high Na content. Due to the low-temperature reaction characteristics of a circulating fluidized bed (CFB), the ash-related problems might be alleviated when ZDc is used as fuel in a CFB. In this study, the slagging and fouling characteristics of three types of ZDc were tested in a 0.4 t/d CFB test system. The influences of three aspects including reaction temperature, reaction atmosphere, and coal property were studied in order to realize the utilization of ZDc in the CFB. Experimental results indicate that slagging and fouling still occurred in the CFB. During gasification, ZDc displayed slagging behaviors in the riser, which was closely related to the used bed material of quartz sand. The slagging degree was increased with the rise of reaction temperature. In different reaction atmospheres, the migration and transformation behaviors of Na differed, which further contributed to the slagging in the riser during gasification and fouling on tail heating surfaces during combustion, respectively. Besides, the Na content and occurrence mode in ZDc greatly impacted slagging. For the used three kinds of ZDc, their slagging tendencies obeyed the order of ZDc-3 > ZDc-1 > ZDc-2.
Conclusions:
In this paper, slagging and fouling characteristics of Zhundong high-sodium coal during circulating fluidized-bed utilization were investigated in a 0.4 t/d CFB test system. The study was chiefly carried out from three aspects of reaction temperature, reaction atmosphere, and coal property. The main conclusions are listed below.
(1) During ZDc gasification, the quartz-sand-induced slagging obviously occurred in the riser, and the issue was enhanced by the increasing reaction temperature. Hence, a low reaction temperature is suggested to avoid slagging when quartz sand is used as the bed material.
(2) Ash-related problems varied with the reaction atmosphere. During combustion, more Na species were released and then condensed in deposits, resulting in obvious fouling on tail heating surfaces, while a stronger slagging was seemingly exhibited in the riser during gasification. Besides, during combustion, finer ash particles were generated and contributed to ash deposition.
(3) Slagging behaviors were greatly influenced by the Na properties including the Na content and occurrence mode. For the used three types of ZDc, their slagging tendencies followed the order of ZDc-3 > ZDc-1 > ZDc-2.
The results have been published on Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 13239-13247.