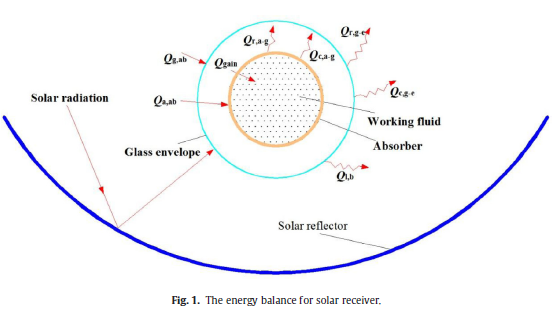
The influences of some parameters on the performance of parabolic trough solar receiver are investigated in the present work. When the mass flow rate of working fluid, ambient temperature and solar incident angle increase, the heat losses of solar receiver decrease. The exergy losses of solar receiver increase as the inlet temperature of working fluid, wind velocity, and the inner diameter of glass cover increase. The convective heat loss of glass cover predominates in the heat losses of solar receiver based on thermal efficiency, but the exergy lost from absorber ends takes the largest proportion. The optical heat loss of solar collector is far more than the heat losses of solar receiver, especially in the larger solar incident angle. There exists an optimal mass flow rate of working fluid for exergy efficiency, and the thermal efficiency and exergy efficiency have opposite changing tendencies under some conditions. Therefore, the selection of evaluation criteria is crucial to the performance optimization of solar collector system. This study is of great significance to guide the design and optimization of parabolic trough receivers.
Conclusions
The influences of some important operation parameters on the performance of solar receiver are investigated in the present work. The comparison between calculated and experimental results shows that the model employed in the present work is reliable in qualitative analysis. The convective heat loss of glass cover predominates in all heat losses of solar receiver, but the exergy lost from the ends of receiver is the largest among the exergy losses of solar receiver due to high temperature. There exists an optimal mass flow rate of working fluid for exergy efficiency, and the thermal efficiency and exergy efficiency have opposite tendencies as the inlet temperature of working fluid and the ambient temperature increase. Therefore, the selection of evaluation criteria is crucial to the performance optimization of solar receiver system. The increase of diameters of glass cover and absorber enlarges the heat transfer area, and the heat losses increase. The wind velocity has adverse effects on the performance of solar receiver, the solar incident angle affects the performance of solar receiver seriously, and the optical heat loss is far more than the heat losses of solar receiver. The optical efficiency improvement of solar collector has important significance on the solar utilization.
The results have been published on Applied Thermal Engineering 95 (2016) 357–364.