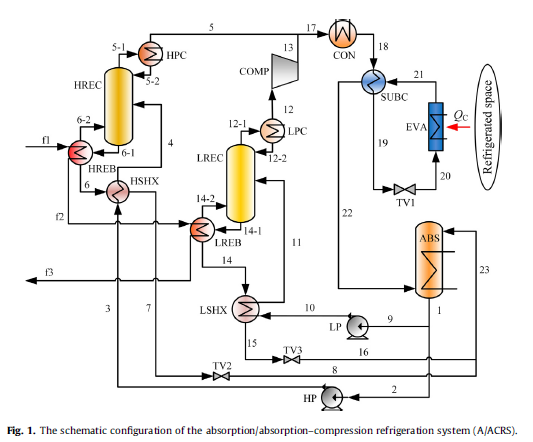
Absorption refrigeration systems are a promising way to reduce electricity consumption in the field of refrigeration and cooling. To improve the thermal energy utilization performance of the absorption refrigeration system, an absorption/absorption–compression refrigeration system with a large working range is proposed in this paper. The new system consists of a conventional single-effect absorption subcycle and an absorption–compression refrigeration subcycle, and they share the condenser, evaporator, absorber and some other relative components. The temperature of the waste gas exhausted from the system can be 35℃lower than that of the waste gas from a traditional, single-effect absorption refrigeration system. For the proposed system, the cooling capacity per unit mass of flue gas reaches 58.95 kJ kg-1 when the evaporation temperature is -15℃, which is 28.21% higher than that of the single-effect absorption refrigeration system. The exergy efficiency of the proposed system is as high as 25.94%. To indicate the direction of system optimization, the new system is further studied using a parametric analysis. The new absorption/absorption–compression refrigeration system provides a promising way to efficiently utilize heat sources with large temperature change or multiple heat sources with different temperatures.
Conclusions
This paper proposed a new absorption/absorption–compression refrigeration system to recover more energy from a variable temperature heat source. A flue gas heat source is utilized in a cascade manner according to the temperature. Multiple heat sources with different temperatures can also be efficiently used in the proposed A/ACRS by slightly modifying the configuration of the heat source. The high-temperature heat was used by the absorption subcycle and the low-temperature heat was utilized by the absorption–compression subcycle. The exhaust flue gas temperature in the proposed system reached 90℃, which is 35℃ lower than that in the conventional absorption refrigeration system. With the same flue gas input, the cooling energy output of the proposed system was increased by 28.21% compared with the conventional system. Furthermore, the exergy efficiency of the proposed system reaches 25.94%. The optimum generation temperatures in the HREB and LREB, and the optimum generation pressure in the LREB have been obtained based on parametric analysis. The proposed system provides a promising way to utilize sensible heat source more efficiently.
The results have been published on Energy Conversion and Management 113 (2016) 153–164.