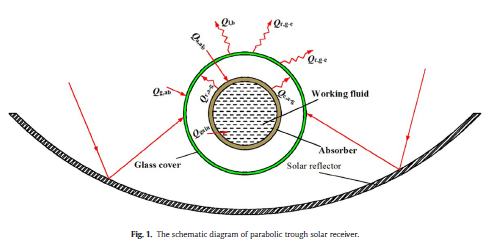
The design parameters of parabolic trough solar receiver are interrelated and interact with one another, so the optimal performance of solar receiver cannot be obtained by the convectional single-parameter optimization. To overcome the shortcoming of single-parameter optimization, a multi-parameter optimization of parabolic trough solar receiver is employed based on genetic algorithm in the present work. When the thermal efficiency is taken as the objective function, the heat obtained by working fluid increases while the average temperature of working fluid and wall temperatures of solar receiver decrease. The average temperature of working fluid and the wall temperatures of solar receiver increase while the heat obtained by working fluid decreases generally by taking the exergy efficiency as an objective function. Assuming that the solar radiation intensity remains constant, the exergy obtained by working fluid increases by taking exergy efficiency as the objective function, which comes at the expense of heat losses of solar receiver.
Conclusions
The optimal performance of parabolic trough solar receiver cannot be achieved by the conventional single-parameter optimization, since the design parameters are interrelated and interact with each other. To overcome the defect of the single-parameter optimization, a multi-parameter optimization of parabolic trough solar receiver is employed based on the genetic algorithm in the present work. When the exergy efficiency is taken as the objective function of optimization, the average temperature of working fluid and the wall temperatures of solar receiver increase generally, while the heat obtained by working fluid decreases. When the thermal efficiency is taken as the objective function of optimization, the average temperature of working fluid and the wall temperatures of solar receiver decrease in general, while the heat obtained by working fluid increases. In comparison with other parameters, the temperature has the greatest effect on the exergy efficiency in the ranges of parameters selected in the present work. The thermal efficiency focuses on the quantity of heat obtained by working fluid, while the exergy efficiency pays more attention to the quality of heat obtained by working fluid. The exergy obtained by working fluid increases by taking exergy efficiency as an objective function at the expense of heat losses of solar receiver.
The results have been published on Applied Thermal Engineering 98 (2016) 73–79.