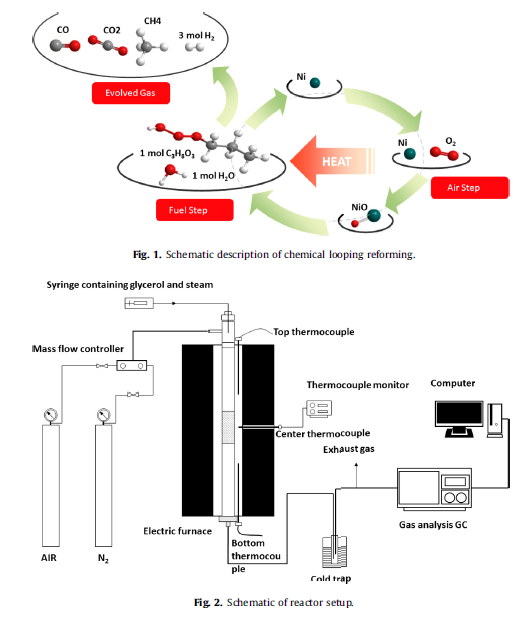
Hydrogen production from chemical looping steam reforming (CLSR) of glycerol was studied by Ni-based oxygen carrier in a fixed-bed reactor. For the fixed-bed reactor configuration, solid Ni-based oxygen carrier is stationary and alternatively exposed to reducing and oxidizing conditions by periodically switching the feed gases. The Ni-based oxygen carrier was prepared by a liquid-state co-precipitation method with rising pH technique and the characterization was performed by X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), transmission electron microscope (TEM) and N2 adsorption-desorption. Gaseous products and temperature variety during CLSR process by Ni-based oxygen carrier in a fixed-bed reactor were measured, and the thermodynamic equilibrium calculation was also carried out. The results showed that the Ni-based oxygen carrier synthesized has a dual function and can efficiently convert glycerol and steam to H2 by redox reactions. The coexisting reactions of glycerol oxidization (or NiO reduction) and steam reforming occurred before the steady stage of hydrogen production in the fuel feed step, and the conversion of NiO to Ni was obtained. Alternating reduction and oxidation reactions enabled Ni-based oxygen carrier to produce H2 with a concentration of 85% of the equilibrium value at 600 ℃, and glycerol conversion was up to 99%. The increase of temperature related to the exothermic reactions by Ni-based oxygen carrier in CLSR process was observed in redox cycles.
The chemical looping steam reforming of glycerol was investigated in a fixed-bed reactor by Ni-based oxygen carrier prepared by the co-precipitation method with rising pH technique. The physical properties of Ni-based oxygen carrier were characterized by BET, XRD, TEM and SEM. The results showed that Ni-based oxygen carrier converted efficiently glycerol and steam to H2 by redox reactions. The H2 concentration of 90% of the equilibrium value was achieved at 600 ℃ and the glycerol conversion was close to 100% in the steady stage of hydrogen production in the fuel feed step. The heat releasing was decreased with the cycles proceeding and the conversion of NiO to Ni was obtained. Compared with conventional SR progress, the CLSR progress showed higher glycerol conversion and H2 yield efficiency in all the tested temperatures.
The results have been published on CHEMICAL ENGINEERING JOURNAL Volume: 280 Pages: 459-467.